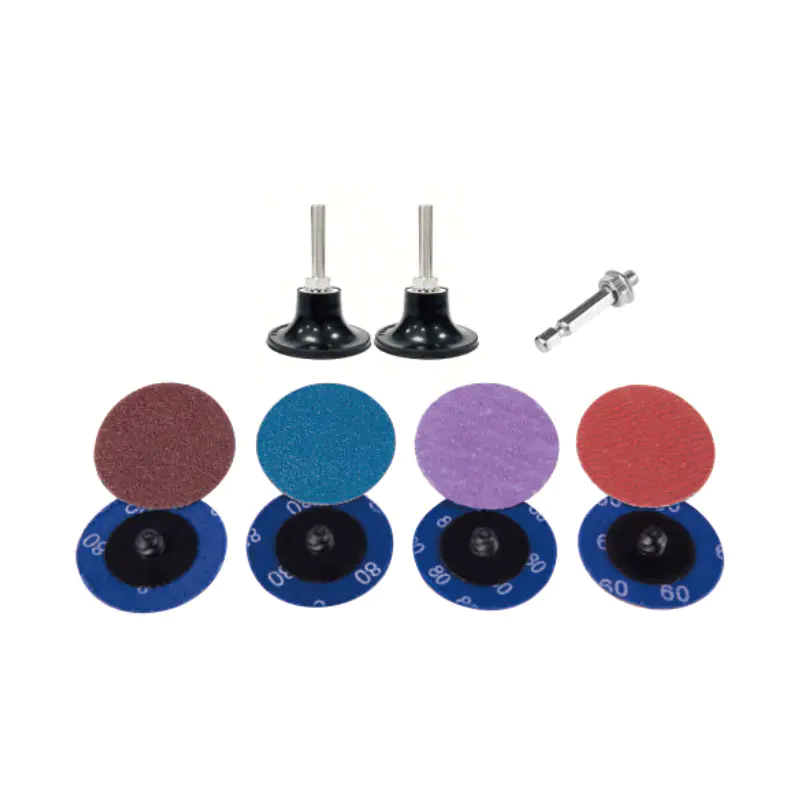
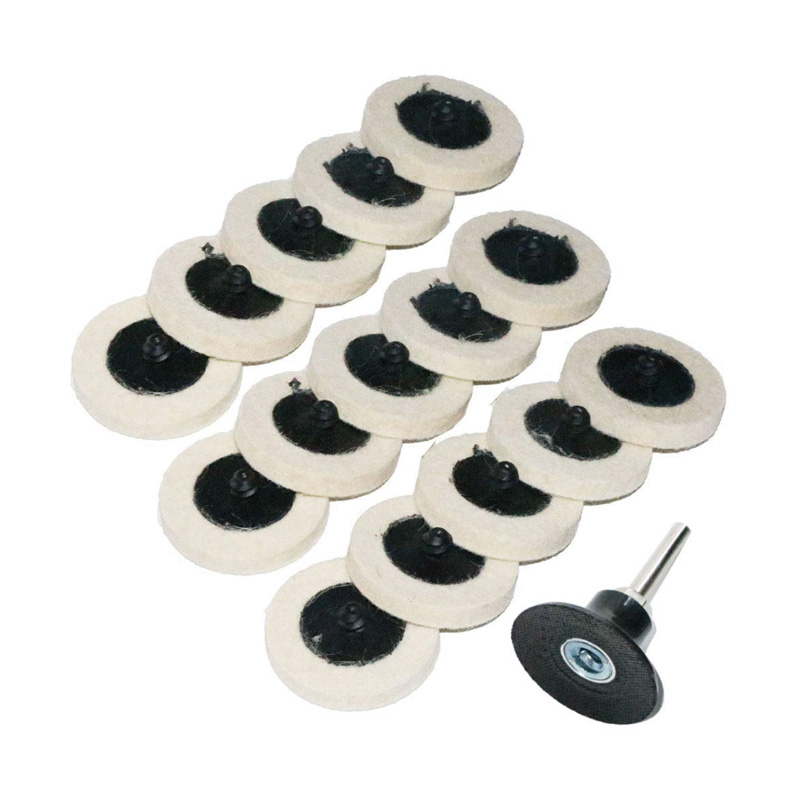
-
0
70
Industry
Experience -
0
50000
Factory
Area -
0
30
Export
City -
0
120
Working
Engineer
We are a premier German abrasive enterprise subsidiary, operating three state-of-the-art factories across 50.000 square meters, dedicated to delivering superior products with excellent logistical connectivity. We are a high-tech enterprise integrating R&D, production, and sales, dedicated to providing customers with high-quality grinding solutions.

We provide customized product services in terms of shape and size to meet the specific needs of different customers.
Our products come with a 3-year protection period to ensure your peace of mind and security during use.
Some products use imported raw materials to ensure high efficiency, safety and environmental protection.
-
2026-01-26
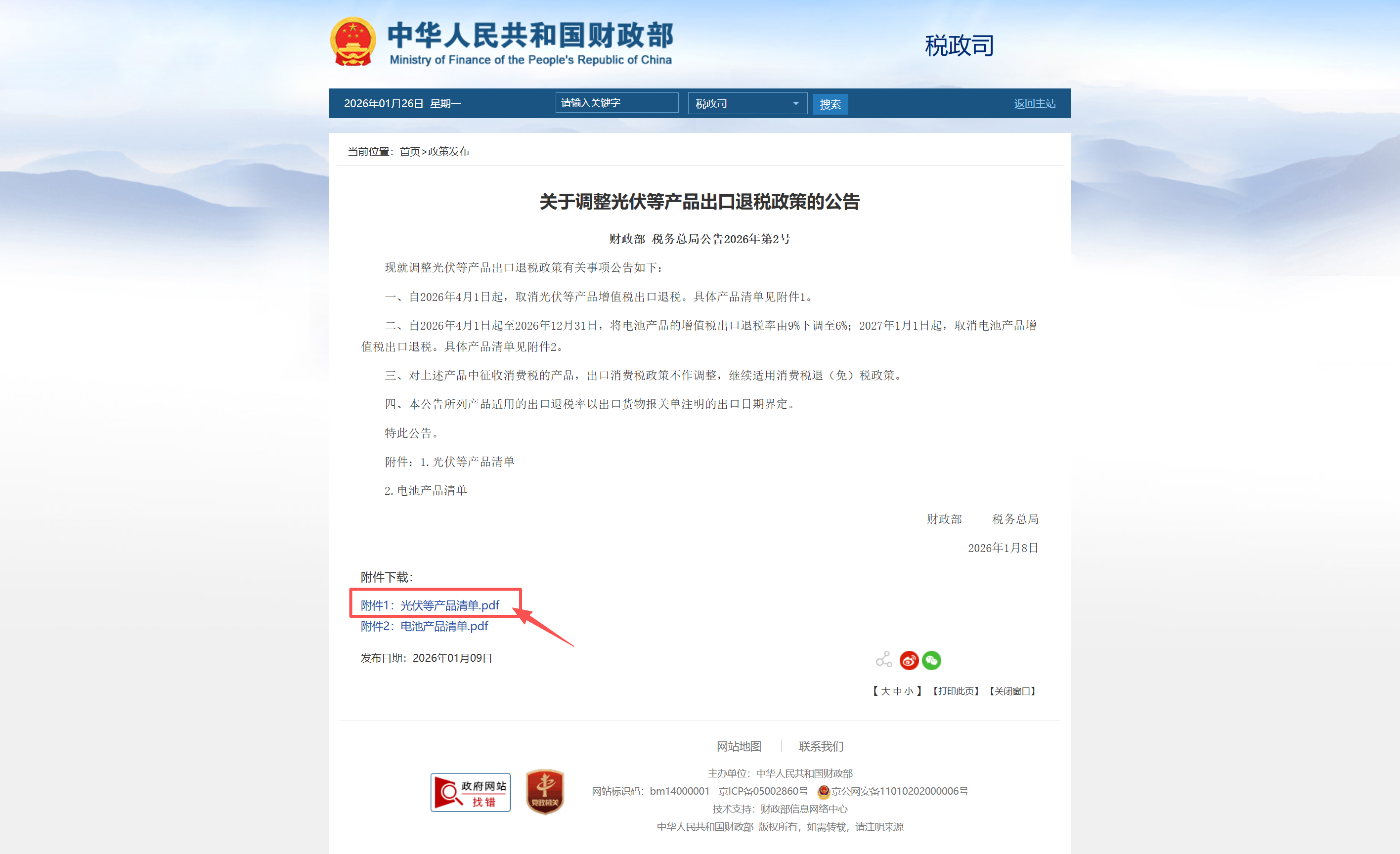
To our dear clients and partners, We are writing to inform you about an important regulatory update that will impact the global abrasives and tools industry. According to the latest statement from China's Ministry of Finance (MOF), effective from April 1, 2026, the export tax refund for a wide range of abrasive products—including cutting discs, grinding wheels, belts and sanding sheets—will be completely withdrawn. You can check the official announcement here: https://szs.mof.gov.cn/zhengcefabu/202601/t20260109_3981637.htm . Consequently, the prices of our products will necessarily be adjusted in line with this policy change. Price updates are already being rolled out progressively. For the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information, please contact our sales team directly. We understand that any price increase presents challenges. However, this shift also encourages an evolution toward greater product quality and technological advancement across the industry, rather than competition based solely on cost. To help you plan effectively: We recommend that you request a timely quote for your upcoming projects and thus receive current price information. Please consider confirming orders in advance where possible, especially before Chinese New Year, to secure production slots and avoid extended delivery times. Our team is available to discuss your needs and provide personalized support during this transition. We appreciate your continued trust and partnership. If you have any questions or require the latest price list, please feel free to contact our dedicated support team. Thank you for your understanding and cooperation. Sincerely, ABRASIVE BUDDIES Your Trusted Partner in Abrasives and Tools
-
2026-01-06
If you still think of abrasives as mere consumables—items to use, wear out, and replace—it's time to take a closer look. The industry is undergoing a fundamental transformation. Over the next decade, abrasives and grinding tools are set to evolve from passive consumables to active, integral technical materials. This change is not about flashier marketing claims; It is a quiet revolution driven by hard data and the relentless demands of global advanced manufacturing. Several recent industry forecasts, including a comprehensive report from Future Market Insights (FMI), point not just to growth, but to a profound and structural shift in the abrasives landscape. To understand the future, we must look beyond general market size figures and examine where and why these changes originate. Europe: The Unexpected Engine of New Standards Although often labeled as a "mature" market, Europe is currently the crucible where new abrasive standards are being forged. Its industrial base is rapidly polarizing towards two demanding sectors: ultraprecision (aerospace, semiconductor manufacturing) and sustainable green production (low-emission and recyclable tools). This double pressure is reshaping product requirements. For example, the expansion of aerospace component manufacturing in Spain and France requires grinding tools capable of achieving micron-level precision. At the same time, the electric vehicle revolution requires new solutions for machining lightweight aluminum and composite materials, driving the need for tools with greater heat resistance and cutting power. Strict EU environmental regulations are forcing a transition towards low-emission binders and longer-life, recyclable abrasive products. The lesson is clear: Europe may not be the fastest-growing market, but it is increasingly the source of the new global benchmark. The Age of Engineered Abrasives The rise of synthetic or manufactured abrasives is a fait accompli. FMI predicts they will account for 65% of the market by 2025. It is no longer simply a matter of “replacing” natural abrasives; Synthetics have become the indispensable basis for modern manufacturing. The key evolution is from "high performance" to fully designable. Synthetic grains enable controlled structure, predictable thermal stability and uniform behavior, crucial elements for their integration into automated robotic cells and CNC systems. In applications ranging from wafer polishing and electric vehicle powertrain machining to aerospace surface finishing, this engineered consistency and traceability is what high-end manufacturers, both European and beyond, value most. The Resurgence of Bonded Abrasives: Driven by Automation It's a surprising trend: Bonded abrasives, such as grinding wheels, are expected to maintain a 48.5% market share in 2025. Why is a "traditional" product category thriving? The answer lies in the global explosion of automated grinding systems. Robotic deburring, automated polishing cells and CNC grinding centers cannot tolerate inconsistencies. They require tools with predictable tool life, stable material removal rates and unwavering reliability. Bonded abrasives, especially vitrified and superabrasive wheels, perfectly meet this need. Its growth is directly linked to the automation of precision tasks in electric vehicle component manufacturing, aerospace preprocessing, and automated powertrain finishing. The Insatiable Appetite for Electronics The electronics sector remains the largest end user, expected to account for 33.4% of demand in 2025. What is significant is not just its size, but its continually growing and evolving requirements. As semiconductors become more complex, wafers thinner, and high-frequency devices more sensitive, demands on precision abrasives intensify. Thinner wafers require more precise microgrinding; intricate chip architectures increase deburring challenges; and tighter surface roughness tolerances are non-negotiable. This creates a "voracious" demand that constantly drives abrasive technology. Given the global nature of R&D in electronics (in Europe/US/Japan) and mass production (in Asia), the abrasives supply chain needs to be updated synchronously around the world. A Fragmented Global Panorama: Three Parallel Trajectories The global market no longer moves uniformly. IMF data reveals three different trajectories: Asia-Pacific (The Capability Hub): Home to the fastest growth rates (e.g. India at 6.4%, China at 4.8% CAGR), driven by expansion in automotive, electronics and new smart factories. Europe and North America (The Standard Setters): Growth here is moderate but structurally advanced, driven by high-end industries such as aerospace, electric vehicles and semiconductors. It is a market defined by precision and regulatory compliance. Middle East (The Fast Emerging Market): Led by Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030, this region shows explosive growth in metallurgy, construction and new industrial bases, representing a new and rapidly rising demand center. Conclusion: The Core is Reconfiguration The central message of the data is not merely market expansion, but a fundamental reconfiguration of the industry's foundations. Automation demands “engineering grade” abrasives as standard. Environmental legislation is revolutionizing chipboard systems. In smart factories, the premium for “predictable lifespan stability” decisively outweighs competition based solely on price. The future of the abrasive industry will be defined by: Seamless Integration: Products that connect effortlessly with robotic production lines. Sustainable Compliance: Formulations that meet strict environmental and carbon standards. Micron Level Consistency: Tools that deliver unwavering precision and reliability. Extreme Performance: Solutions that maintain their integrity under high speed and high temperature conditions. We are witnessing a pivotal transition. Abrasives are moving beyond their commodity status to become a core enabling technology. Partnering with a supplier that understands this shift is the first step to securing your competitive advantage in the future of manufacturing.
-
2025-11-24
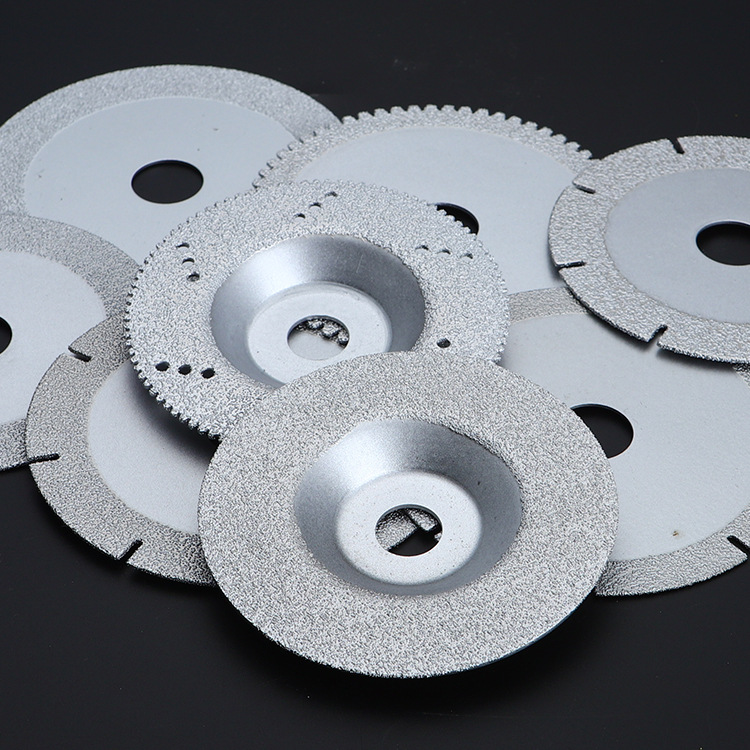
In the vast landscape of industrial manufacturing, few tools are as crucial yet as inconspicuous as the diamond grinding wheel. In simple terms, a diamond wheel is a superabrasive tool composed of diamond grains bonded by a metallic, resinous, ceramic or electroplated matrix, forming a solid circular structure with a central hole. Although its appearance may be simple, its internal architecture is an engineering marvel, typically consisting of three integral parts: the diamond abrasive layer, the transition layer, and the core. Each layer plays a distinct but collaborative role, allowing the wheel to perform high-efficiency grinding tasks with exceptional precision. Deconstructing the Diamond Grinding Wheel: A Trio of Performance Think of your structure as a precision team where each member has a specific role: The Abrasive Layer: The Cutting Edge This outer layer is the warrior on the front line. Contains diamond abrasives, binder and filler materials. Diamond grains, the hardest material found in nature, act as the primary cutting force, effortlessly machining hard and brittle materials. The binder material acts as a powerful adhesive, holding the diamonds firmly in place and providing structural integrity and shape stability. Fillers are added to improve performance, such as increasing wear resistance or reducing grinding forces. The Transition Cloak: The Unsung Hero Located between the abrasive layer and the core, this layer is the critical bridge. Made from a mixture of binder and filler materials, it is not involved in grinding but is vital for safety and durability. Dramatically improves the bond strength between the abrasive layer and the core, preventing the abrasive ring from coming off under high rotation speeds and immense grinding forces. It is the essential security lock that ensures overall stability. The Core: The Solid Foundation Typically made of aluminum, steel or composite materials, the core is the backbone of the entire grinding wheel. It holds the abrasive layer and mounts securely to the grinding machine spindle using a flange. A high-quality, well-balanced core minimizes vibration and noise during high-speed operation, which is critical for superior grinding accuracy and finish. Why Diamond Grinding Wheels Stand Out: Unmatched Properties Diamond wheels outperform conventional grinding wheels due to a combination of exceptional properties: Exceptional Hardness and Cutting Capacity: The supreme hardness inherent to diamond allows these wheels to easily grind challenging materials such as tungsten carbide, advanced ceramics and optical glass, significantly increasing productivity. Superior Wear Resistance: Diamond grains wear very slowly, ensuring consistent grinding performance over a much longer lifespan compared to standard wheels. This reduces downtime due to wheel changes and lowers long-term operating costs. High Precision Machining: Minimal wear of the diamond grains allows the wheel to maintain its shape and cutting profile. This stability is indispensable in precision manufacturing, allowing critical tolerances in industries such as aerospace and semiconductor manufacturing. Low Grinding Force and Excellent Thermal Conductivity: These wheels typically generate less force on the workpiece, reducing the risk of deformation or damage. Additionally, diamond's excellent thermal conductivity helps dissipate heat quickly, preventing thermal damage such as burns or microcracks in the finished surface. Wide Applications: A Key Tool in Various Industries The unique properties of diamond wheels make them indispensable in modern manufacturing: Aerospace: Used for precision grinding and finishing of high-strength components, such as jet engine turbine blades, where extreme precision and surface integrity are non-negotiable for safety and performance. Tool and Mold Manufacturing: Essential for creating and maintaining high precision molds and dies from hardened steels, ensuring the quality and efficiency of mass production processes for plastics, stamping and casting. Semiconductors and Electronics: Criticisms in the production of silicon wafers and other components. According to a report from the Precision Manufacturing Group, diamond grinding is a key step in wafer thinning, allowing for precise thickness control and minimal subsurface damage, which directly increases wafer performance. Optical Manufacturing: They allow ultra-precision grinding and polishing of optical glass and crystals, achieving nanometric-level surface finishes required for high-performance lenses and laser components. Stone and Construction: A traditional and widespread application, diamond wheels are the preferred solution for efficiently cutting, shaping and polishing natural and artificial stone, from granite countertops to architectural elements. As a leading manufacturer of high-performance abrasives, including cutting wheels, grinding wheels, sanding belts and related accessories for power tools, we leverage advanced diamond tool technology to provide our global customers with reliable and efficient grinding solutions. Explore our range of products to discover how we can improve your manufacturing capabilities.
-
2025-11-07
The Istanbul Hardware Fair is back, and this year it's bigger and more innovation-oriented than ever. From November 19 to 22, 2025, industry leaders, engineers and trade professionals will gather at the Istanbul Expo Center to explore the latest advancements in tools, equipment and materials solutions. As a trusted manufacturer and exporter of high performance abrasives and power tool accessories, BUDDIES is pleased to announce our participation in this premier event. You can find us at Booth 4A19-2, where we will showcase cutting-edge solutions designed for durability, efficiency and real-world applications. Why Visit BUDDIES at the Fair? Whether you work in metal fabrication, woodworking, automotive, or general construction, you understand the importance of reliable abrasives. The right cutting wheel, grinding wheel or sanding belt can dramatically impact productivity, finish quality and operating costs. At our booth, you will experience first-hand what makes BUDDIES a reference brand for professionals around the world. 1. Precision Engineering Cutting and Grinding Wheels Our cutting and grinding discs are manufactured under strict quality control standards. With reinforced resin binders and high-purity abrasive grains, they offer fast cutting, smooth grinding and extended life, even under high-pressure conditions. 2. Versatile Coated Abrasives: Sanding Belts and Sheets From coarse grinding to fine finishing, our line of coated abrasives includes sanding belts, sheets and rolls tailored to a variety of materials. Using electrolytic aluminum or zirconium oxide grains, these products resist dulling and provide consistent performance on wood, metal and composite surfaces. 3. Angle Grinders and Accessories Performance doesn't stop with abrasives. We also supply compatible angle grinders and essential accessories optimized to work perfectly with our discs and blades. Ergonomics, power and safety are built into every tool. Strategic Position: Türkiye's Growing Market and Exposure Advantages Türkiye's unique geographical position, spanning both Europe and Asia, makes it a crucial bridge between eastern and western markets. This strategic location has established Turkey as a manufacturing and distribution hub, with easy access to markets in Europe, the Middle East and North Africa. The country's industrial sector continues to expand rapidly, and the abrasives and tools market is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 5.2% through 2028, driven by strong infrastructure development and manufacturing investments (reference: Global Market Insights, 2023). The Istanbul Hardware Fair capitalizes on this strategic advantage, serving as the most important trade platform in the region. For international suppliers, it offers unrivaled access to distributors, manufacturers and industrial buyers throughout the region. The exhibition provides a unique opportunity to understand regional requirements, establish local partnerships and showcase products to a diverse and growing market. What Makes BUDDIES Your Ideal Partner? While many manufacturers offer standard abrasive solutions, BUDDIES offers exceptional value through: Complete Product Portfolio: From cutting and grinding discs to sanding belts, rolls and specialized power tools, we offer comprehensive solutions for various industrial applications, eliminating the need for multiple suppliers. Heritage of German Quality: Building on the technical legacy of Rhodes Germany, we maintain uncompromising standards in material selection and manufacturing processes, ensuring superior performance and reliability. Strategic Industry Partnerships: Our collaborations with global leaders such as 3M, VSM and NORTON allow us to incorporate the best technologies and industry standards, offering products that meet the most demanding professional requirements. Rigorous Testing and Customization: Each product undergoes strict quality control and we offer tailored solutions to address specific application challenges. Join Us at Booth 4A19-2 We invite you to stop by our booth, try our products and discuss your specific needs with our technical and commercial teams. Whether you're a distributor, contractor, or industrial end user, we're here to help you work smarter
-
2025-10-31
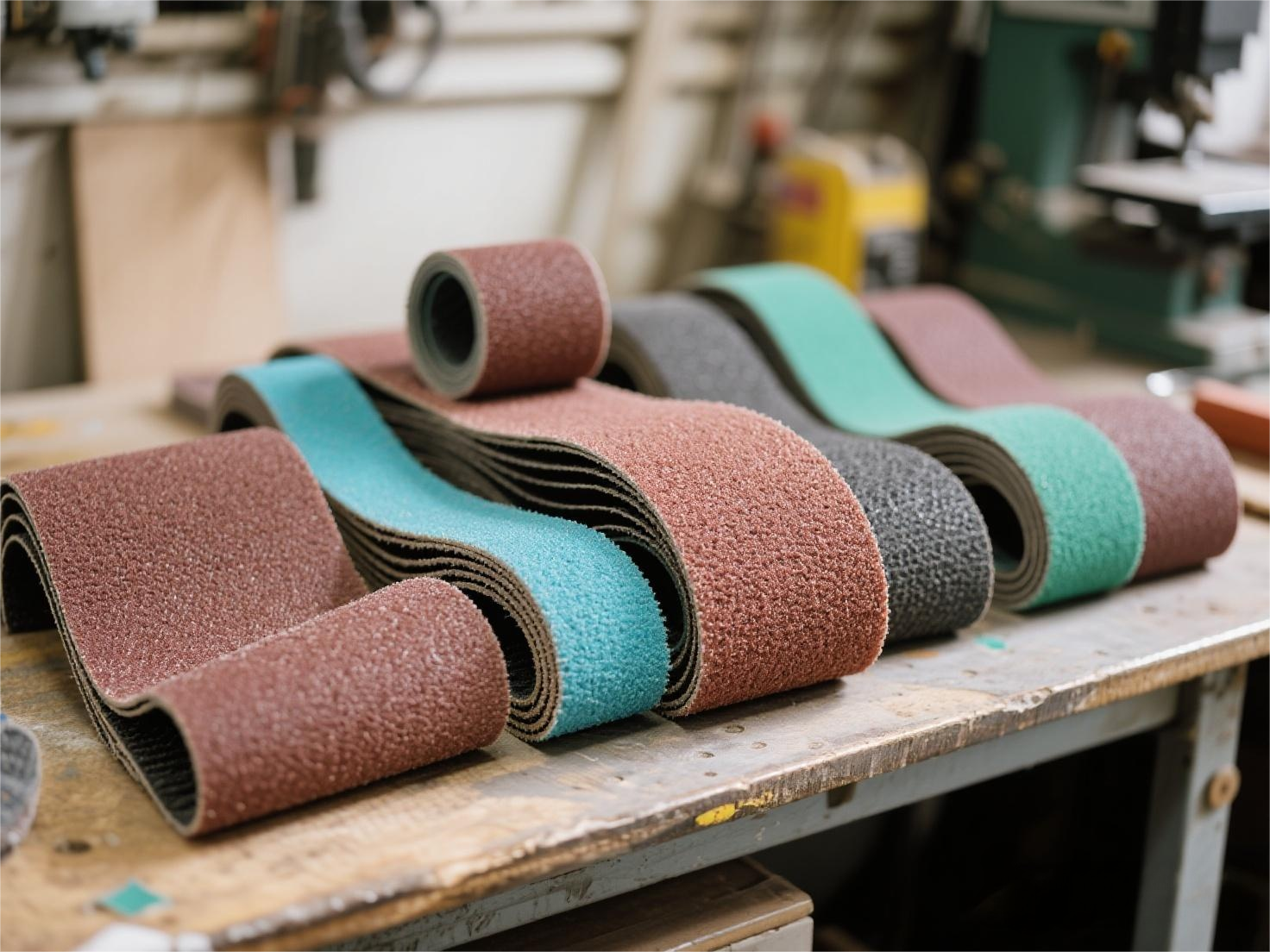
In the world of abrasive tools, sanding belts stand out as versatile workhorses for everything from metal polishing to woodworking. But what makes them durable, flexible and efficient under intense pressure? The answer lies in its base structure: the backing fabric. Often overlooked, this critical material determines how well a belt performs during cutting, grinding or finishing tasks. As a leading exporter of cutting discs, grinding wheels, sanding belts, sandpaper and angle grinder accessories, we have seen first-hand how the right backing fabric can elevate product quality and customer satisfaction. This guide delves into the characteristics of backing fabrics used in coated abrasives such as sanding belts. We will explore material types, historical innovations, key performance factors and practical selection criteria. Whether you are a manufacturer optimizing production or a buyer looking for reliable tools, understanding these elements ensures you get the most from your abrasives. Let's break it down step by step. Why Backing Fabrics Matter in Sanding Belts The backing fabrics provide the structural support for the abrasive grains in the sanding belts. Unlike rigid bases, these fabrics offer flexibility, allowing the tape to conform to curved surfaces without cracking or tearing. They must resist high tensile forces, withstand the heat generated by friction, and bond flawlessly with adhesives and grains. Common materials include cotton, polyester, and blends such as cotton-polyester blends. Cotton remains the preferred choice for its affordability and ease of processing, while synthetics address limitations such as poor water resistance. The choice depends on the application: heavy-duty industrial grinding belts favor robust polyester, while lighter polishing tasks suit cotton. Globally, backing fabrics vary by weight and weave to match grain sizes and workloads. Heavier fabrics excel at coarse grits and aggressive sanding, distributing force evenly to prevent premature wear. The lighter ones shine in fine grains, offering a smoother finish without excessive flex. Standards differ by region: American manufacturers might grade by grams per square meter (gsm), while European standards focus on tensile strength, but the principle is universal: tailor the fabric to the job for optimal longevity and efficiency. Evolution of Backing Fabrics: From Cotton Classics to Synthetic Powers Cotton has dominated backing fabrics since the early days of coated abrasives, thanks to its natural advantages. Obtained abundantly and cost-effectively, cotton fabrics provide a smooth, uniform surface that bonds well with resins, glues and grains. Their high flexibility prevents buckling during tape flexing, and they offer solid tensile strength with minimal elongation under load. However, cotton's disadvantages—such as its lower resistance to water and heat—fueled innovation. In the 1960s, the United States pioneered nylon-based sanding belts, marketed as Microlon, which increased grinding efficiency by approximately 20 times compared to traditional cotton versions. This advancement was due to nylon's superior durability in wet conditions and high-speed operations. In the 1970s, polyester fabrics emerged as a game changer. With higher tensile strength, lower stretch rates, and better heat and moisture resistance, polyester enabled heavier-duty tapes for demanding applications such as finishing aerospace parts or automotive metal machining. The Norton company's polyester-backed tapes quickly gained popularity worldwide, driving rapid adoption. Today, polyester represents 7-8% of backing fabrics in coated abrasives in developed markets, with the United States reaching 13.5% as early as 1981—a figure that has continued to increase (source: Coated Abrasives Manufacturers' Institute Industry Reports, 1982). Blends, particularly cotton-polyester blends introduced using Japanese and Korean technologies in the late 1990s, have increased in popularity in China and beyond. These hybrids combine the processability of cotton with the tenacity of polyester, offering thick, flat fabrics at competitive prices. To illustrate the improvement, consider the physical properties of the 3M company data on cotton versus polyester backings: These metrics highlight why polyester dominates in high-load scenarios: less stretch means precise control, while low water absorption prevents delamination in humid environments. Key Requirements for High Quality Backing Fabrics Selecting the right backing isn't a guessing game - it's guided by precise specifications tailored to the performance of the sanding belt. Here we show you what to prioritize: Fiber Type: Balancing Strength and Compatibility Cotton reigns supreme in 80-90% of coated abrasives due to its prowess in bonding with various adhesives, flat surface for uniform grain coating, high strength with low stretch and low cost. It is ideal for standard dry sanding. Synthetic options like nylon or polyester come in for specialized needs. They offer smoother surfaces and unmatched strength, but they can elongate more and require selective adhesives—for example, animal glues do not adhere well to synthetic glues. Advances in pretreatments, such as high-temperature stretching, have minimized these problems, making polyester a staple for waterproof tapes. Cotton-polyester blends address mixed demands: cotton helps adhesion, while polyester boosts durability. In China, these have proliferated since the 2000s, but their processing requires dual treatment methods to manage the different fiber affinities—cotton needs saturation for glue absorption, polyester favors surface activation. Cotton and Quality Blend For cotton-dominated fabrics, fiber quality is non-negotiable. Premium long-staple cotton—fine, mature and free of impurities—produces denser, whiter, stronger fabrics with minimal knots. This results in tapes that resist tearing during aggressive uses. In blends, fiber ratios matter: a 60/40 cotton-polyester blend could optimize cost and strength, but the ratios must align with the end use. Poor mixing leads to uneven wear, so rigorous testing is essential. Grading by Weight: Adapted to Grain and Task Like paper backings, fabric weights are graduated for specific roles. Heavier weights (e.g. 300-500 gsm) accommodate coarse grits (16-60) in power grinding, absorbing impacts without fraying. The lightest ones (150-250 gsm) fit fine grits (120 gsm) for polishing, ensuring flexibility without sinking. Ratings vary: US standards may use "J" for medium-heavy (based on FEPA standards), while others reference ISO weights. For sheet abrasives, lighter fabrics are sufficient; The tapes demand the heaviest ones for tear resistance. Always consult manufacturers' charts for exact matches. Knitting Structure and Thread Count Twill weaves dominate with their balance of thickness, softness and strength—perfect for embedding grains without compromising flexibility. Finer twills (higher thread counts, thinner threads) produce elegant surfaces for fine grain tapes, ideal for mirror finishes on metals. Thicker twills (lower counts, thicker threads) handle rough sanding, providing bulk for durability. Plain weaves occasionally appear in ultra-fine applications because of their flatness, aiding polishing on delicate substrates such as composites. Density, Strength and Elongation: The Performance Triad Optimal density strikes a middle balance: too dense, and the fabric hardens, hindering glue penetration; too loose, and it weakens, absorbing excessive adhesive. Aim for balanced fabrics that maintain softness along with robustness. A high warp density with a lower weft density promotes radial strength for tape tension, while easier weft tearing simplifies sizing in production. Low elongation (less than 10%) is crucial—elastic fabrics distort under load, leading to uneven abrasion and tape failure. BUDDIES Professional Perspective: Engineering Wisdom in Backing Material Selection At BUDDIES, we firmly believe in the industry truth that "backing sets the ceiling, while abrasives unlock performance." Our technical team recommends: For metal machining and standard woodworking, premium twill cotton fabrics offer reliable solutions with excellent flexibility and cost-effectiveness. In humid environments or coolant-intensive operations, polyester backings exhibit superior stability, resisting delamination and maintaining integrity. For heavy-duty grinding and high-volume production, advanced synthetic fiber backs ensure efficiency, minimizing downtime and maximizing performance. We maintain rigorous supplier control and incoming inspections to ensure that each roll of sanding belt backing meets our performance standards. Our experts are always available to offer personalized backing selection advice, helping you match the ideal sanding belt to your specific workpiece materials, machinery configurations and precision needs. Partner with BUDDIES today—let's engineer your next advancement in abrasive performance.
-
The “Steel Skeleton” of Cutting Discs: Revealing How Fiberglass Mesh Improves Safety and Performance2025-10-15
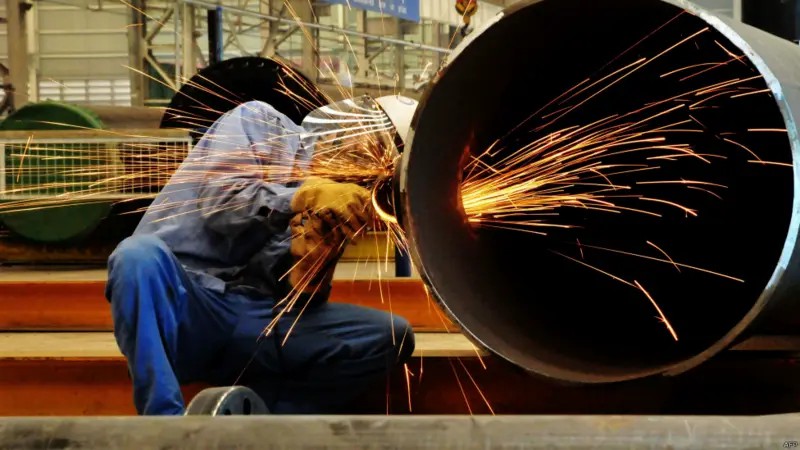
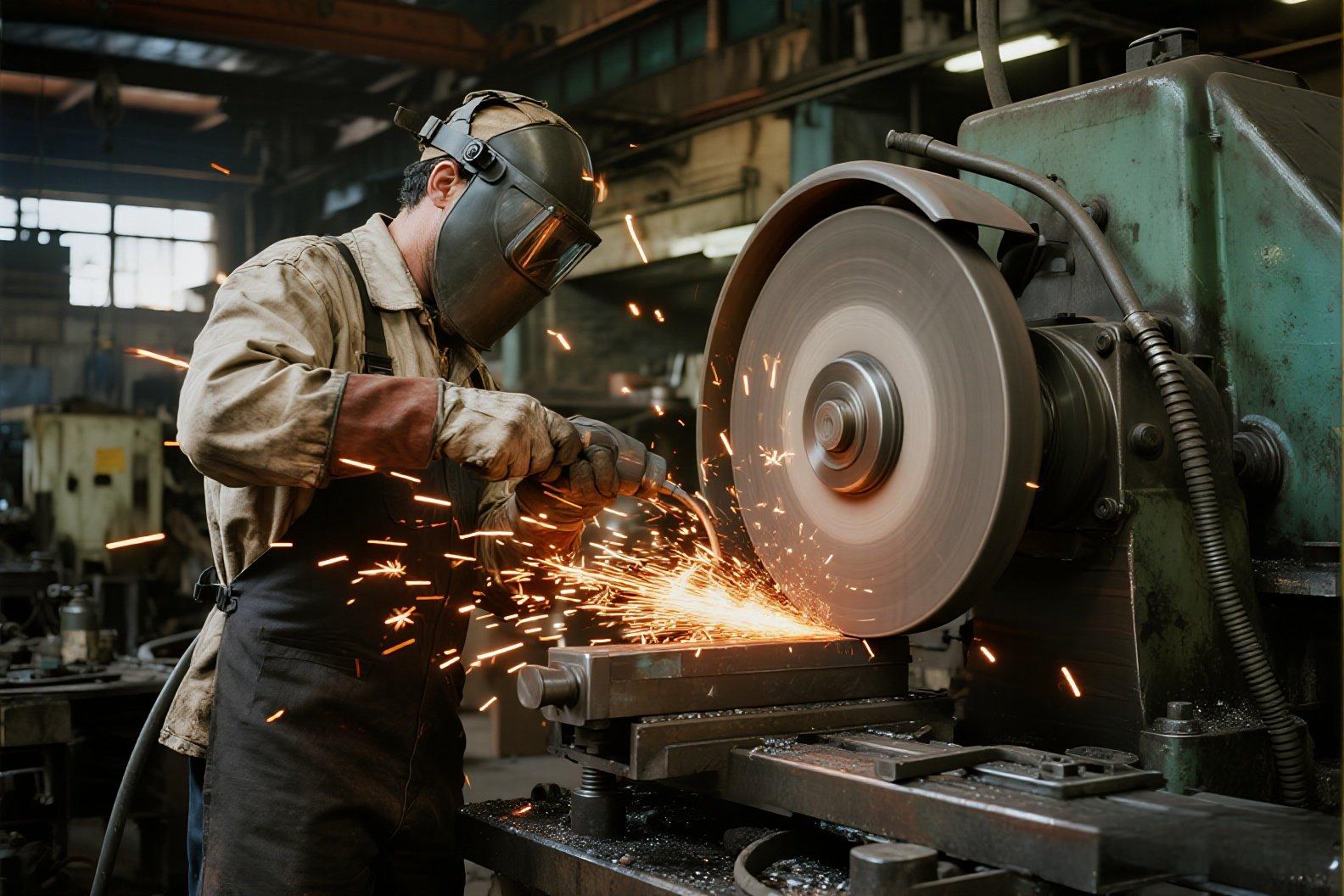
When you hold an angle grinder and sparks fly when cutting metal, have you ever wondered why that thin cutting wheel, rotating at high speed, can withstand such centrifugal forces and immense impacts? The secret often lies in its seemingly simple structure. Beyond the abrasive surface and the internal resin, the real unsung hero is the reinforcing mesh sandwiched in the middle: it is the "steel skeleton" of the cutting disc. Today, as a technical expert at BUDDIES, we take you on an in-depth exploration of this fiberglass mesh, revealing how it becomes the foundation of safety and performance in our line of abrasives. I. What is Mesh in a Cutting Disc? – Lessons from Reinforced Concrete Imagine a cutting wheel as a slab of reinforced concrete: the abrasives (such as aluminum oxide or silicon carbide) act as the tough "concrete" for the cut, while the reinforcing mesh serves as the interlocking "steel bars," providing structural support and reinforcement. This mesh is typically positioned in the center of the disc, seamlessly integrated with the abrasive layers through advanced manufacturing processes. Its presence transforms the inherently brittle nature of the disc into a high-strength, high-impact composite material. II. Why is it essential? – The Four Main Missions of Fiberglass Mesh Maximum Security: The Lifeline Against Breakage This is the most critical role of the mesh. Cutting discs operate at speeds greater than 10,000 RPM, withstanding massive centrifugal stresses. Without reinforcement, sudden changes in cutting force or jamming in the workpiece could cause stress concentrations that lead to catastrophic failure. The fragments would scatter like bullets, posing serious risks to operators. Backed by data: According to European standard EN 12413, cutting wheels must withstand overspeed tests at 1.6 times their rated RPM without failing. The fiberglass mesh is key here, absorbing and distributing stresses effectively. Even in rare breakage scenarios, it binds the fragments together, preventing dangerous projectiles and maximizing operator protection. Mechanical Strengthening: Withstands Higher Speeds and Pressures The fiberglass mesh has exceptional tensile strength, acting as a resilient fishing net that supports the brittle abrasive layer. This allows the discs to tolerate higher operating pressures and rotational speeds, ideal for demanding industrial tasks. At BUDDIES, our heavy-duty cutting discs incorporate high-weight, high-density meshes to ensure unwavering stability during long, intense use. Improved User Experience: Reduction of Vibrations and Deformations A single-layer mesh provides basic reinforcement, but for harsher conditions, double-layer or multi-layer composite structures excel. Increasing the layers significantly improves the rigidity of the disc, controlling vibrations and oscillations at high speeds. Benefits include: Precise Cut : Less deviations in the groove for cleaner results. Comfortable handling : Less fatigue in the operator's hands. Less Tool Wear : Smoother on angle grinder bearings, prolonging the life of the machine. Assistance in Heat Dissipation and Chip Removal The open mesh structure is not completely dense, creating tiny channels for airflow and debris expulsion. This helps mitigate heat buildup in the cutting zone, extending blade life and maintaining efficiency. III. Materials and Layers: BUDDIES Engineering Choices What materials are used for the mesh? Fiberglass : The undisputed leader in cutting discs, offering unmatched advantages: High Tensile Strength : Individual strands reach 1,000-3,000 MPa—2-3 times that of common steel. Superior Heat Resistance : Withstands prolonged exposure to 550°C and short bursts above 700°C, perfectly adapted to the intense heat of cutting. Excellent Insulation : Prevents electrical risks during operation. Corrosion Resistance : Antirust and durable in various environments. Low-cost alternatives like cotton thread or nylon mesh fail in strength and heat tolerance, posing real safety risks. All BUDDIES cutting discs—from our PRO series to everyday options—use premium fiberglass meshes for unbreakable safety. Other materials, such as polyester or nylon, appear in ultra-thin discs for handling and molding support, but pale in mechanical reinforcement compared to fiberglass. How to Choose the Number of Mesh Layers? The layer count is directly linked to the degree of performance and application. BUDDIES designs align with this engineering principle: Single Layer Mesh : For standard uses such as DIY projects or cutting low carbon steel—essential safety and basic strength at an economical price. Double Layer Mesh : The brand of professional and industrial discs, providing superior rigidity, resistance to bending and protection against ruptures. Ideal for frequent, heavy-duty tasks such as construction sites, metal fabrication or stainless steel work. Our PRO series of BUDDIES features predominantly double-layer fiberglass structures for elite performance in adverse conditions. Multilayer/Special Structures : For large diameters (≥400 mm) or specialized applications, complex multilayer reinforcements counteract exponentially greater centrifugal forces. IV. The Hidden Craftsmanship: The Signature Touch of BUDDIES Premium mesh is just the start; The true excellence lies in fusing it with the abrasive layers. BUDDIES employs specialized resin impregnation and automated pressing systems, ensuring that the resin fully saturates each fiberglass strand for a flesh-and-blood-like chemical bond. This adhesion remains strong even under extreme tests, unlocking the full potential of the mesh's "steel skeleton." Conclusion: Your Security, Our Foundation When selecting cutting wheels, look beyond price and aesthetics—the invisible fiberglass mesh sets the baseline for safety and the ceiling for performance. Although it does not cut directly, it is the silent guardian that ensures that each cut is smooth, efficient and safe. At BUDDIES, safety is our vital essence. From selecting high-strength fiberglass cloths, to optimizing single- and double-ply designs, and refining precision manufacturing, every disc we produce boasts a reliable "steel skeleton." Because we understand: the tools in your hands connect not only materials, but a commitment to professionalism and responsibility. Explore our range of cutting discs, flapping discs, abrasive belts and angle grinders at buddiesabrasives.com—empower your projects with BUDDIES today.
-
2025-09-29
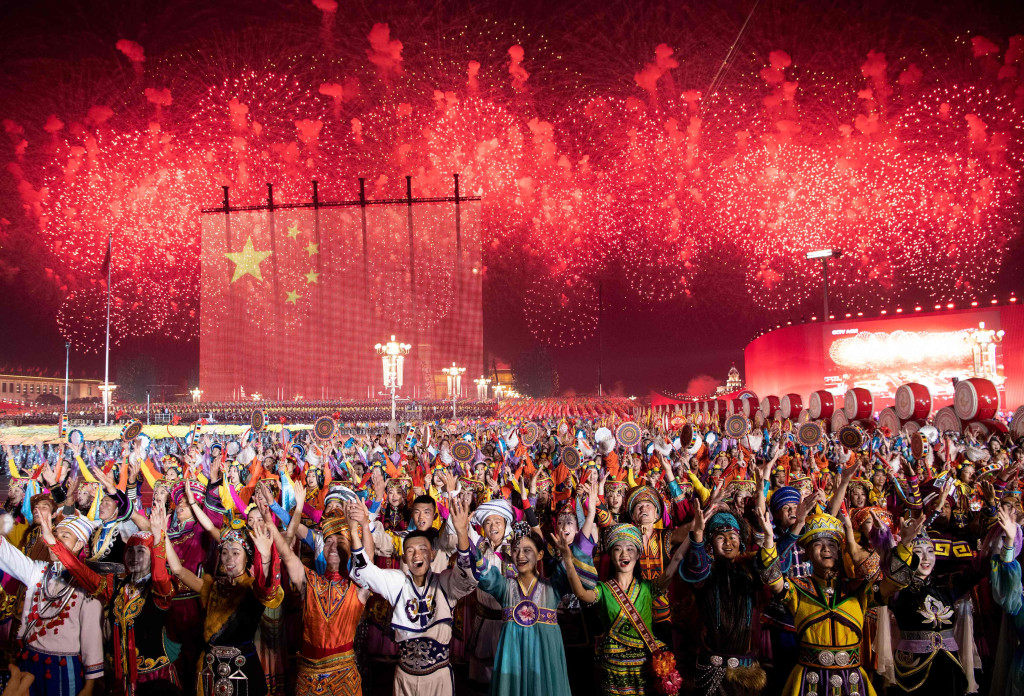
When the golden fall involves China in a festive splendor, the nation celebrates the 76th anniversary of the People's Republic of China, a moment loaded with pride and the enduring spirit of the revolution. Buddies, a committed actor in the abrasive industry, is proud to contribute to China's manufacturing power with cutting discs, abrasive teeth, sandpaper bands, sandpaper and accessories for angular grinders. The parades of the National Day, with impeccable formations and imposing teams, exhibit the industrial force of China, lighting the pride of each citizen. However, behind these monumental achievements are anonymous heroes: abrasive, humble but essential tools, which shape the precision and power of China's great creations. Abrasive tools never claim the care center. They do not have the roar of the fighters or the majesty of the aircraft carriers. But, like the anonymous heroes of China's revolutionary past, these tools play a crucial role in each key stage of the modern industry. Imagine the cylinder of a tank engine: to withstand extreme heat and pressure, its internal surface must reach a smooth mirror and precise roundness, possible thanks to the precision rectified. Missile guide systems require impeccable optical lenses, without scratches or dust, to ensure millimeter precision to thousands of kilometers - this depends on ultrafine polishing. The turbine blades of the fighters, turning tens of thousands of revolutions per minute, resist heat and extreme vibrations thanks to high resistance surface treatments. Submarine propellers, sliding silently through deep seas, need efficient and stealthy performance to evade sound - looked through a meticulous rectified and polished. In the aerospace field, abrasive tools are invisible artisans that shape China's "heavenly dreams." From Chang’e lunar missions to Martian Tianwen exploration, satellite and rocket components require impeccable surface finishes to support the hard conditions of the space. Processes such as the elimination of oxide layers in titanium alloys, the ultra -proven valve rectified and the machining of narrow grooves in turbine blades depend on tools such as electrochapaded CBN toothes, CBN CBN wheels of ceramic junction and PCD tools. These instruments embody the revolutionary ethos of precision and excellence, allowing the Chinese ships to furrow the cosmos. In naval construction, abrasive tools reinforce the maritime sovereignty of China. Navy ships, patrolling vast oceans, depend on the dripping with steel granalla to eliminate oxide and improve corrosion resistance, ensuring their availability in turbulent seas. This reflects the revolutionary spirit of protecting the homeland, from the anti -fascist war to the current maritime strength. For poachers, specialized abrasives polish curved surfaces until reaching a mirror finish, minimizing the reflection of radar waves and improving the invisibility - a testimony of the tireless search for perfection rooted in revolutionary ideals. In the manufacture of military equipment, abrasive tools are the spine of reliability. The components of nuclear submarines are reinforced with high strength granallado, increasing fatigue resistance to ensure strategic dysmuase in deep water. Tanks offices require a precise rectified to guarantee mobility on difficult land. These thorough processes directly impact the performance of the team, reflecting the resilience of the revolutionary pioneers who built the industrial base of China from scratch, transforming it into a global manufacturing power. Beyond defense, abrasive tools shine in civil industries. The High Speed Railroad of China, a national connectivity symbol, depends on wheels and precise rectified rails to guarantee stability at 350 km/h. This commitment to security reflects the revolutionary principle of prioritizing the people. From metro tunnel drilling tools to wind turbine blades, abrasives silently hold the rise of Chinese infrastructure, acting as progress torches in the industrial saga of the Nation. On this national day, we reflect on the enduring power of revolutionary culture. From the Jinggangshan spark to the challenges of the long March and the winds of the reform, perseverance has defined the spirit of China. The abrasive tools, although small, embodied this legacy - each rectified won the rough, each polishing pursues perfection. They support extreme conditions to refine China's manufacturing excellence. Looking ahead, the abrasive industry evolves with China's technological advances. Ecological rectified techniques, intelligent machinery and abrasive materials of nanometric precision inject vitality to Chinese manufacturing. In the global stage of the Strip and the Route initiative, these tools empower world industries, carrying out the revolutionary values of self -sufficiency, innovation and excellence. On this national day, Buddies pays tribute to the anonymous heroes of Chinese manufacturing. Through the meticulous work of abrasive tools, we forge the greatness of the creations of our nation; Through the legacy of revolutionary culture, we turn on the way to national rejuvenation. Buddies wishes everyone a happy day and a prosperous and flourishing China!
-
2025-09-03
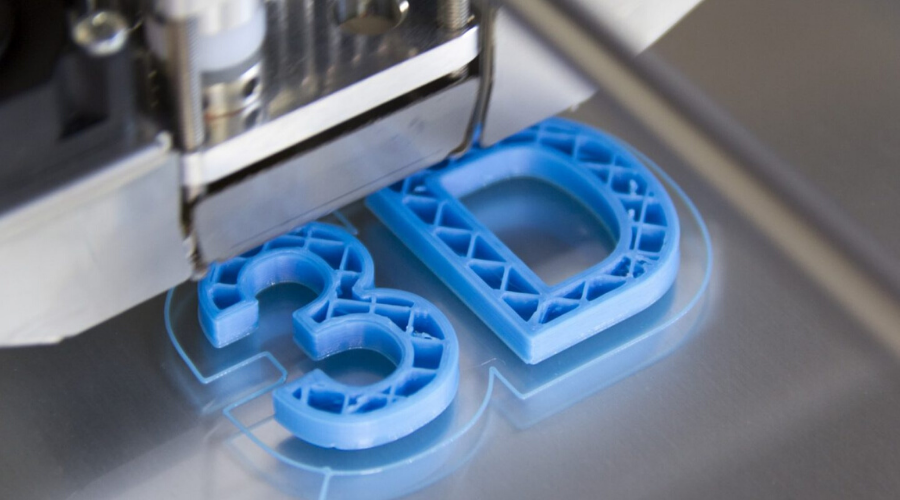
In the current manufacturing panorama, the 3D impression stands out for its flexibility and customization capacity. It allows designers and engineers quickly transforming concepts into physical models, with automotive, medicine and aerospace applications. However, 3D printed parts usually have rough surfaces, with visible layer lines or defects that do not meet professional standards. This is where postprocessing is essential. Through specific surface treatment techniques, the aesthetics, mechanical performance and the functionality of the pieces can be significantly improved. This article explores several postprocessing techniques to achieve soft surfaces, offering practical advice for beginners and professionals. Why do 3D printed parts need postprocessing? 3D printing is based on layer manufacturing, either by FDM (molten deposition modeling), SLA (stereolithography) or SLS (selective laser sintering). This process leaves cape lines or granular textures. According to industry data, unreasonable pieces have a superficial roughness (RA value) of 10-50 microns, while postprocessing can reduce it to less than 1 micra, achieving almost mirror finishes. The postprocessing has multiple objectives: eliminate layer lines, soften surfaces, improve corrosion resistance, refine dimensional precision and prepare parts for paint or assembly. The choice of the method depends on the material (plastic, metal or resin), the complexity of the piece and the budget. Next, we detail the most effective techniques. Manual or mechanical sanding: a simple but effective method Sanding is the most accessible and economical postprocessing technique, ideal for plastic and resin pieces. Physically imperfections to obtain a uniform and soft finish. Start with the right tools: Thick grain sandpaper (80-120) to eliminate layer lines, going to fine grains (400-2000) to polish. Manual sanding is ideal for small parts, while electric sanders or vibratory machines speed up batch processing. Steps: Clean the piece: Use alcohol or a soft cleaner to remove waste. Thick sanding: sanding gently following the layer lines to avoid deformations. Intermediate sanding: Use wet sanding with water to reduce dust and improve softness. Final polishing: Apply polishing compound with a cloth for a bright finish. Key advice: controls the dimensions during sanding. For pieces with strict tolerances (eg, ± 0.1 mm), leaves a margin of 0.2-0.5 mm to avoid sanding in excess, which can weaken or deform thin wall pieces. Sanding is laborious but versatile, ideal for DIY fans. Sand and granallado jet: Professional optimization for metal pieces For 3D -printed metal parts, such as aluminum, titanium or stainless steel, sand jet and granallado are highly effective. These techniques use high -speed particles to refine surfaces. The sand jet uses abrasive media (eg, aluminum oxide or glass pearls) to eliminate oxide and soften textures, ideal for aesthetic improvements and coating preparation. Manages complex geometries without damaging internal structures. The granallado, meanwhile, uses metal balls to induce compression voltage, improving the useful life and resistance to cracks, common in aerospace components. Equipment: A sand or granallado jet cabin is needed, with protection equipment to avoid dust inhalation. Control parameters such as pressure (50-100 psi) and particle size (100-300 meshes) to avoid superficial damage. Compared to sanding, these methods are faster (minutes per piece) and automated, but require greater initial investment. For example, an automotive supplier reduced the roughness of RA 20 microns at ran 5 micro with a lease jet, improving product competitiveness. Vibratory and drum polishing: ideal for batch processing To process multiple pieces simultaneously, vibratory polishing and drum are excellent options. These techniques use mechanical movement and abrasive media (eg, ceramic pearls or plastic pellets) to generate friction and achieve uniform finishes. The vibratory polishing places the pieces in a vibratory container with media and lubricant, using high frequency vibrations (thousands per minute) to eliminate burrs. Drum polishing, suitable for larger pieces, is performed on a rotating drum. Both may include chemical additives to accelerate the process, with time treatment times. Advantages: Efficient for batch production and complex forms, with uniform brightness. The disadvantage is the least effectiveness in intricate internal channels. Wash the pieces after polishing to remove waste. In the manufacture of medical devices, these techniques are used in 3D printed implants to guarantee sterile and soft surfaces that reduce infection risks. Steaming by steam and submersion in solvent: chemical routes for a bright finish Steam softwide is an ideal contact without thermoplastic contact such as ABS or ASA. It exposes the solvent vapor pieces (eg, acetone), causing the surface to be slightly and flow, creating a bright finish. Process: Heat the solvent in a sealed camera, suspending the piece for minutes. An alternative is the submersion in solvent, but time must be controlled to avoid excessive dissolution. This method is fast (5-30 minutes) and produces mirror surfaces, but it is not suitable for all materials (eg, PLA can deform). Security note: operates in a well ventilated area to avoid exposure to vapors. Compared to physical methods, steam softwad is more uniform, but can slightly alter the dimensions, ideal for applications not precise as prototypes or decorations. Epoxy resin coating: sealed and strengthening The epoxy resin, a reactive polymer, is applied as a coating or infiltrator in 3D printed parts. Fill microporos, creating hermetic and impermeable surfaces, in addition to improving heat and chemical resistance. Application: brush, spray or infiltrate resin. After the cure, the surface is soft and lasting, ideal for functional parts such as pipes or housings. Tip: Sand the piece before applying epoxy for better results. Use low viscosity resin for uniform coverage and respect cure times (normally 24 hours). Hybrid manufacturing: combining additive and subtractive techniques Modern manufacturing adopts hybrid approaches, integrating 3D (additive) impression with CNC machining (subtractive). Milling or turned after impression eliminates precision rough layers, achieving high quality surfaces. Hybrid machines, which combine laser and CNC fusion, can reduce production cycles by more than 30%, ideal for high -end applications. Conclusion: Elevate your 3D impressions with the appropriate postprocessing With these techniques, you can transform printed pieces into rough 3D into professional quality products. The key is to choose the method according to the material, use and budget, prioritizing security and precision. Start with small -scale tests to perfect the process. If your company offers 3D printing services, mastering these techniques can differentiate.
-
2025-08-26
In the demanding sectors of the automotive, the marine and the high -end manufacture, choose a high -performance polishing tool is crucial to achieve higher results and optimal operational efficiency. The Buddies sanding disk stands out as a revolutionary solution, combining avant -garde technology with a practical design that meets the needs of professionals. Designed for a precise surface finish, this album shines in the repair of automotive paint, the refinement of marine coatings and the polishing of high quality furniture, offering bright finishes and without defects easily. Its unique capacity for dry and humid guarantees versatility in various applications. You are already a specialist in Automotive Oem, a marine maintenance technician or a furniture craftsman, this sanding album is your definitive solution. Next, we explore its features, applications and prominent advantages. Product description: innovation and durability The Buddies sanding disc is made of advanced precision coating and microstructured replication technologies. Its main abrasive, silicon carbide, is distributed in a microscopic pyramid pattern on a 3,000 polyester film backup (0.076 mm). This uniform and repetitive structure ensures consistent sanding performance, delivering precise and efficient results. The disk has a pressure sensitive adhesive backup (PSA), which allows rapid and safe fixing to portable points sanders, optimizing the workflow in intense production environments. Designed for flexibility, the disc offers a variety of specifications to adapt to various tasks. Grain sizes range from A3 to A9, supporting a progressive sanding from the elimination of thick material to ultrafine polishing. The diameters vary from 19 mm to 76.2 mm, ideal for small defect repairs and larger surface treatments. Coded color options (grayish, gray, green, purple) facilitate task differentiation, improving operational efficiency. With a maximum speed of 10,000 rpm, it maintains stability in high intensity tasks. According to the Buddies product sheet, the discs are packaged in rolls of 500 units, with 50 rolls per box, perfect for wholesale purchases and inventory management. An outstanding aspect is its dry and humid sanding capacity, which eliminates the need for abrasive sludge. This ensures a clean and efficient process, reducing powder and environmental impact while maintaining performance in dry and humid conditions. Its water -resistant design and its anti -obstruction structure make it a sustainable option for modern industries. Versatile applications: solutions for each industry Automotive industry In the preparation and repair of automotive paint, the Buddies sanding album offers exceptional results in varnishes, paintings and plastics. Effectively eliminates paint defects, microparticles or pollutants, ensuring a smooth base for subsequent processes. For example, during paint preparation, professionals can start with an A3 grain to level rough surfaces, advance A9 for a fine polishing and end with a foam pad and polished compound for a bright finish, achieving a car body with an exposure room quality. Marine maintenance In marine applications, the disc refines vessel coatings, improving corrosion resistance and visual appeal. Its impermeable properties make it ideal for wet sanding, offering uniform results on large or contoured surfaces, such as yacht helmets or ship components, even in challenging marine environments. High -end furniture finish For high quality furniture, such as pianos or pieces of luxury wood, the disc provides a bright and protective finish. Softens wood or coated surfaces, handling flat designs and curves with ease, which makes it perfect for manual or mechanical sanding in furniture workshops. General industry and painting preparation In broader industrial environments, the disc prepares metal, plastic or compounds for coatings, improving the quality of the final product. Its microstructured design expels waste, avoiding obstructions, which is crucial for high volume production lines where efficiency is fundamental. Unmatched advantages: efficiency, durability and cost savings The Buddies sanding album offers convincing benefits that distinguish it. Its microstructured design extends the useful life of 2 to 3 times compared to traditional abrasive papers, reducing the frequency of replacement and inactivity time. The dry and humid sanding capacity eliminates the need for abrasive sludge, reducing material costs and maintaining a clean work space, which minimizes health risks due to exposure to dust. Industry data suggests that reduce polishing costs by 20% –30% compared to abrasive films. Its versatility is an outstanding feature. With multiple grain sizes and diameters, it supports a progressive sanding, reducing surface roughness to micrometric levels for a mirror finish. The impermeable design improves the efficiency of wet sanding, especially in automotive and sea applications, while its clean operation reduces waste, aligning with ecological production objectives. This combination of durability, versatility and sustainability makes it a profitable option for companies of all sizes. Practical tips for optimal use To maximize performance, it starts with lower grains (for example, A3) for the initial elimination of material and advances to the finest grains (for example, A9) for polishing. In wet sanding, apply a minimum amount of water to improve the results. Keep the speeds below 10,000 rpm to guarantee the safety and longevity of the disk. Always use protection equipment, such as masks and glasses, to avoid dust inhalation. Store discs in a fresh and dry environment to preserve their quality. Why choose Buddies? The Point Sanding disc redefines surface polishing with its innovative technology, unique versatility and cost efficiency. From automotive repair workshops to marine maintenance and high -end furniture studies, delivers consistent and high quality results. Visit the Buddies website today for more details or request a sample to experience the future of first -hand polishing. Raise your surface finish with Buddies!
-
2025-08-12
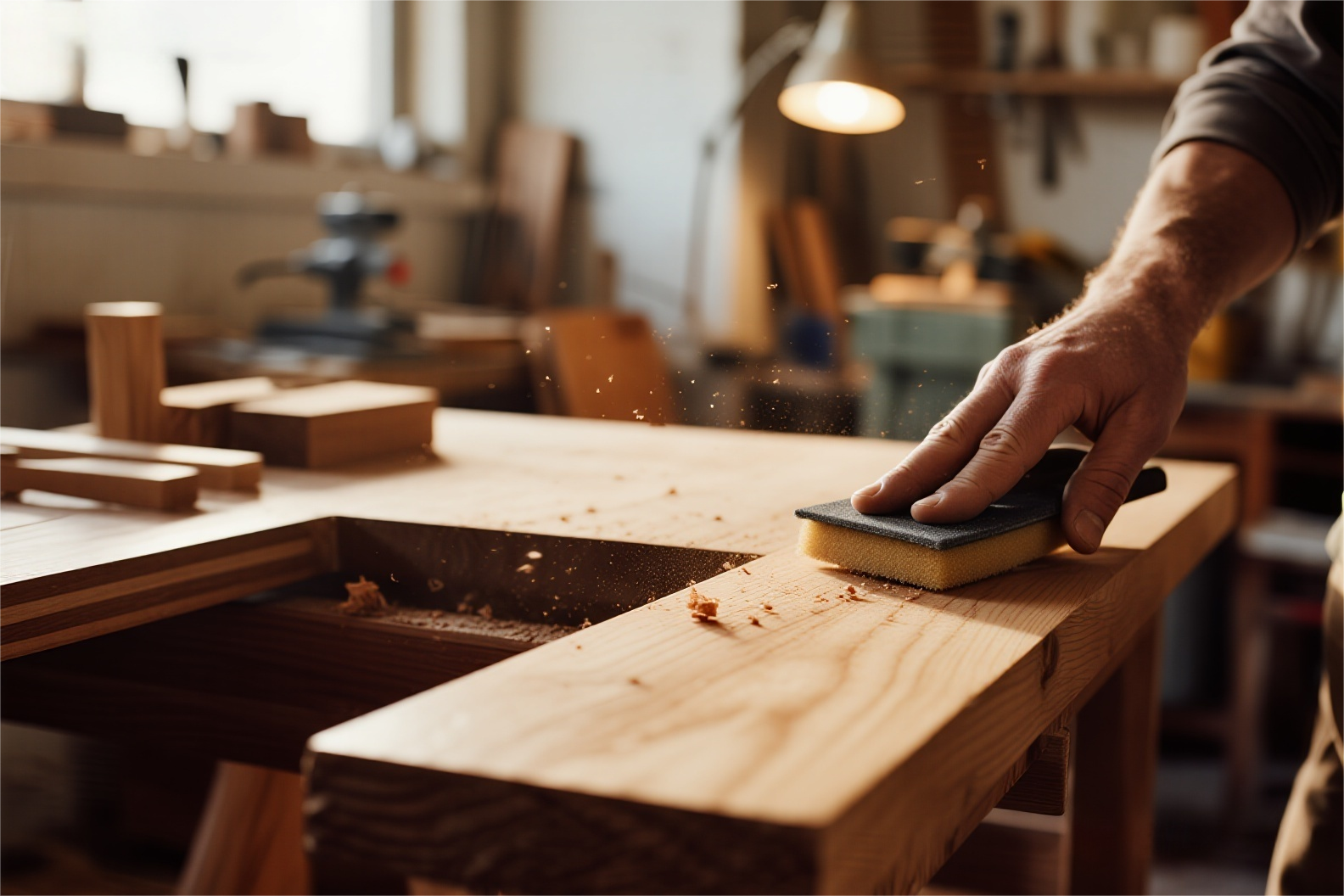
Why do the sanding determine the quality of the finish? Sanding is a fundamental stage in the furniture finish, since it directly influences the final result. A quality sanding sets the bases for an exceptional finish, offering the following benefits: 1. Elimination of imperfections: Removes, oxide, oil and dust from wood surfaces, creating a clean base for coating. 2. Greater superficial softness: the surfaces with putty are usually rough; Sanding alisa to get a uniform finish. 3. Adhesion improvement: smooth surfaces reduce the adhesion of coatings; Sanding favors mechanical union for lasting finishes. Sanding is present throughout the finishing process, from the preparation of gross wood and putty application to the refining of primer and final paint layers. It is a key step to guarantee a bright and resistant finish. Practical techniques for effective sanding Achieving a high quality sanding requires skill and attention to detail. Next, some practical recommendations: 1. Choose the proper grain of sandpaper: Avoid using too thick paper or a single type of grain. Do not jump between grains (for example, from 200# to 600# or 800#), since this can leave visible marks. 2. Set in the direction of the vein: always sanding the vein of the wood to avoid tangrans that affect the aesthetics of the finish. 3. Protect edges and details: Sanding corners and edges softly to maintain its original shape, whether round or square. Decorative lines must remain straight, without bending or break. 4. Correct handling of sandpaper: hold the paper with four fingers and the palm, ensuring the edges with the thumb. For large surfaces, use a block of wood or soft pad, sanding along the vein. 5. Clean during sanding: the generated dust can be embedded in the vein; Use a dry brush to constantly remove it and achieve a smooth surface. 6. Repair minor damage: for scratches or abolish, apply hot water and an iron to restore the surface before sanding. Avoid sanding large areas only with fingers so as not to create irregularities. 7. Sanding of curved parts: on arched or curved surfaces, use a template that matches the shape to hold the sandpaper. If you use electric or pneumatic sanders, follow the curves of the piece to avoid staggered surfaces. Versatile sanding methods Depending on the characteristics of the piece and the needs of the project, different sanding methods can be used: 1. Dry sanding: It is done with sandpaper on hard and fragile surfaces. Its disadvantage is the generation of dust, so attention should be paid to the hygiene of the environment. 2. Wet sanding: Use sandpaper with water or soap to reduce marks, improve softness and save effort and paper. Considerations: Make sure the surface is completely dry before applying the following layer of paint to avoid whitening. Do not use wet sandpaper in very absorbent substrates. 3. Mechanical sanding: For large areas, electric sanders (disc or vibratory) increase efficiency, but require control to avoid excessively sanding. 4. Soft sanding: In cases such as sealants, repainted with old films or partial repairs, a “soft sanding” with fine paper and expert hands is required so as not to damage the surface. Selection and use of sandpaper 1. Selection of sandpaper grain Sanding paper grain directly affects the sanding result. Choose according to the process of the process: Gross wood: sandpaper 180#–240# Initial plywood or sandpaper: sandpaper 220#–240# Straight straightening: sandpaper 320#–400# Final Printing: Seach paper 600#–800# Final layer polishing: sandpaper 1500#–2000# 2. Sanding paper use techniques Manual sanding: cut the sandpaper into four parts, fold it and hold it with the thumb and piss, pressing with the other fingers to sand evenly. Flexible adjustment: Adapt the position of the fingers to sand concave, convex or edges with precision. Land of large surfaces: use the highest point as a reference, pressing with the palm or a sponge/wood pad to maintain uniformity. Safety caution: Keep your nails at an adequate length to avoid injuries during sanding. Causes and solutions for sanding brands 1. Causes Sand against the vein, damaging the texture of the wood. Use too thick sandpaper or sanding before the coated coating. Slow drying solvents that delay the solidification of the coating. Too thin upper layers that do not cover sanding marks. Incomplete cleaning after sanding, leaving dust that affects adhesion. Clogged sandpaper, losing efficacy and causing irregular marks. 2. Solutions Select adequate grains: thicker for the initial sandpaper, thinner for later passes, eliminating previous marks. Always sanding in the direction of the vein to preserve the wood. Make sure the coatings are dry before sanding and cleanses the dust. Check the sandpaper for obstructions and change it when necessary. Adjust the viscosity of the paint and apply thick layers to cover marks. Conclusion Sanding is the soul of the furniture finish, defining both its aesthetic attraction and the durability of the coating. With the proper selection of sandpaper, expert scientific methods and techniques, you can significantly raise the quality of your furniture. Although mechanization progresses, the precision and flexibility of manual sanding remain insurmountable. Dominate these techniques and take your finishes at the next level!
-
2025-08-01
What is a sharpening stone? A sharpening stone is an essential tool in the abrasive industry, designed to grind, sharpen and polish materials such as metal, wood or stone. Also known as grinding stone in certain contexts, it acts as a robust version of the sandpaper, transforming disabled tools into precise instruments or smoothing surfaces until you get a fine finish. Its use dates back to thousands of years: archaeological evidence in Cuddie Springs, Australia, show their use more than 30,000 years ago to process seeds and tools (Australian Museum). Today, they are fundamental both in traditional crafts and in modern manufacturing. Types of sharpening stones: composition and shapes Composition of sharpening stones Aphillary stones are manufactured with natural or synthetic materials. The natives, such as sandstone or novaculite (for example, Arkansas stone), are valued by their unique textures. Synthetic, made of abrasives such as aluminum oxide or silicon carbide, offer consistency and durability, ideal for industrial applications. Abrasive particles are kept together by binders that determine their resistance and performance: Vitrified junction: made of clay or ceramics, is resistant to heat and lasting, suitable for heavy grinding. Resin Union: flexible and impact resistant, ideal for high speed or precision tasks. Metal union: used in superabrasive stones (such as diamond or CBN), designed to cut hard materials. Forms of sharpening stones The sharpening stones have various ways according to their purpose: Wheels: Circular stones mounted on high speed grinding machines, common in factories. Blocks: rectangular or planes, perfect for manual sharp, such as knife stones. Discs: thin stones and flat for precision cuts or surface finishes. APPLICATIONS OF AFILAR Piedras How to use sharpening stones Use depends on the shape and purpose of the stone: Manual grinding: For block form, apply water or oil as a lubricant to reduce friction. Hold the tool at a constant angle (for example, 20 ° for knives) and slip with soft and controlled movements. According to Takahashi Kusu, the thick stones ( 1000 grains) achieve polished edges (Takahashi Kusu). Mechanical grinding: the wheels are mounted on machines that operate at high speeds. Operators must guarantee alignment and cooling to avoid overheating. Applications by material Natural stones: used in traditional trades, such as sharpening carpentry tools or grinding grains in old cultures. Aluminum oxide stones: Common in metallurgy, such as disrupting automotive parts or aerospace component modeling. Silicon carbide stones: Ideal for hard materials such as ceramics or glass, used in electronic manufacturing. Maintenance and use tips To maximize performance and useful life: Cleaning: Rinse with water after using to remove waste. For oil stones, use a soft solvent. Storage: Guard them in a dry and dusty place. Use protective cases for portable stones. Use Tips: Maintain consistent pressure and angle to avoid unequal wear. For wheels, verify the balance to prevent vibrations. Flattened: Stones can develop grooves over time. Use a flattened stone or abrasive plate to restore the surface. Conclusion The sharpening stones are fundamental for the precision and efficiency in the abrasive industry. From sharpening knives to end industrial components, they offer unmatched results. Contact us to discover our range of high quality fraying stones adapted to your needs!
-
2025-07-09
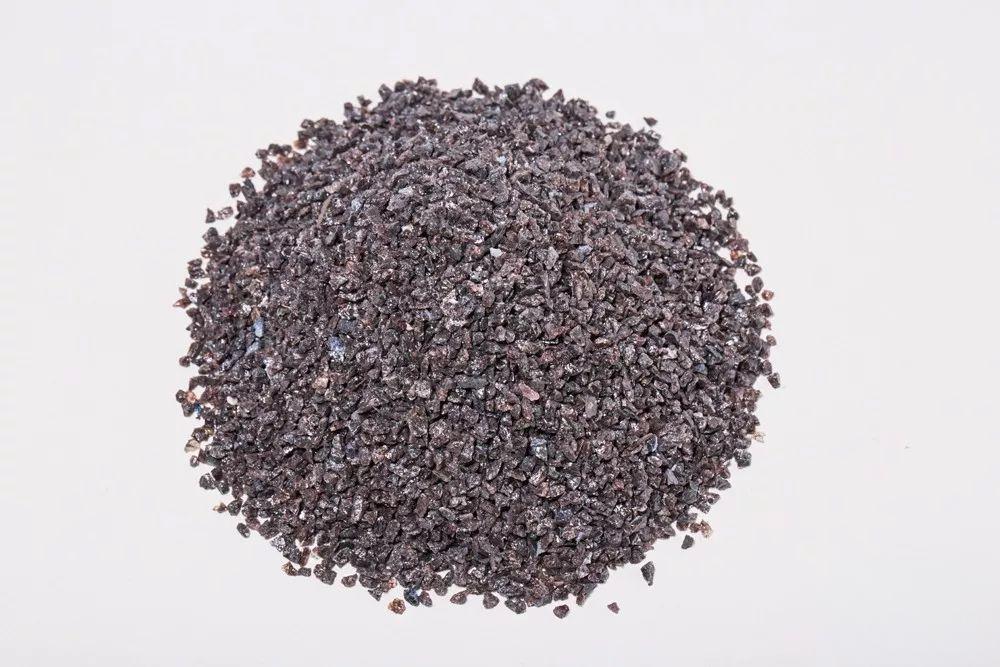
1. Characteristics of abrasives TObrasives are fundamental materials in grinding and polished processes, recognized for their ability to shape and refine surfaces. Its properties, such as hardness, structure and union agents, play a key role in their performance in various applications. Type of abrasive Code Characteristics Applications Rank of use Brown aluminum oxide A High tenacity, excellent wear resistance, profitable Ideal for general grinding of metal materials Suitable for the processing of common metal pieces such as steel and iron White aluminum oxide Wa High hardness, purity and resistance superior to wear Perfect for precision grinding and surface finishing, especially in hard materials Suitable for stainless steel and high hardness alloys Monocrystalline aluminum oxide SA Dense crystalline structure, highly durable Used for high precision and polishing grinding of special pieces Ideal for precision molds and manufacturing complex components Microcrystalline aluminum oxide Ma Microcrystalline structure, exceptional wear resistance Adequate for ultraprecisa grinding and complex surface treatments Perfect for optical glass and components of precision instruments Black silicon carbide C High hardness, strong cutting power, profitable Ideal for grinding of non -metallic materials such as glass and ceramics Suitable for the processing of glass and ceramic items Green silicon carbide GC Extremely high hardness, high purity, efficient cutting Perfect for high precision processing of non -metallic materials Ideal for semiconductor materials and optical components Brown aluminum oxide (Pa) PA Good durability, low cost Suitable for general industrial grinding and surface treatment Ideal for the raw rectified of large -scale metal pieces 2. Hardness The hardness of a grinding tool refers to the ease or difficulty with which abrasive grains are detached from their surface under external force. The tools with grains that emerge easily have a low hardness, while those with firmly adhered grains exhibit high hardness. In China, the hardness of grinding tools is classified into seven main levels and 14 sub -levels. The choice of proper hardness depends mainly on the hardness of the material to be processed. Other factors to consider include the contact area between the tool and the workpiece, the shape of the piece, the grinding method, the cooling techniques and the type of union agent used. 3. Structure The structure of a grinding tool describes the density or spacing of abrasive grains within it, generally expressed as the percentage of abrasive volume. A densest structure, where grains are less likely to detach themselves, helps maintain the shape of the tool and is ideal for grinding, heavy grinding or intermittent tasks. On the other hand, a more loose structure prevents grain dullness, improves cutting efficiency, generates less heat during grinding and reduces the risk of burns or deformations in the piece. This makes it suitable for soft but resistant materials, heat -sensitive components, thin parts or grinding with large contact areas. 4. Union agents Union agents act as the adhesive that connects abrasive grains, forming a grinding tool with a defined geometric shape. The most common union agents include ceramics, resin and rubber. Ceramic Union agents (previously encoded as "A", now "V") are widely used thanks to their high porosity, upper grinding efficiency, minimum wear and ability to maintain the geometric shape of the wheel. This makes them the most popular option in the industry. 5. Grain size Grain size selection for a grinding tool depends on the desired surface finish of the piece and production efficiency requirements. Different grain sizes are adapted to specific applications, guaranteeing optimal results according to quality and production needs. Application range according to grain size: 36# ~ 100# : Ideal for thick grinding, perfect to shape and eliminate material on hard surfaces. 120# ~ 150# : Suitable for intermediate finishing, offering a balance between efficiency and superficial softness. 180# ~ 240# : Excellent for fine finish grinding, providing a softer finish in delicate pieces. 240# ~ W20 : Perfect for precision grinding, ensuring high quality finishes in complex components. W20 (Ultra-Fino) : Optimal for ultrafino polishing, achieving a mirror finish in sensitive materials.

 英语
英语 西班牙语
西班牙语 中文简体
中文简体